Cataract surgery is one of the most common and successful procedures performed worldwide. Millions benefit from improved vision each year, but achieving optimal results hinges on a crucial element: accurate intraocular lens (IOL) power calculation. Without precision in this step, patients may face suboptimal outcomes or even complications.
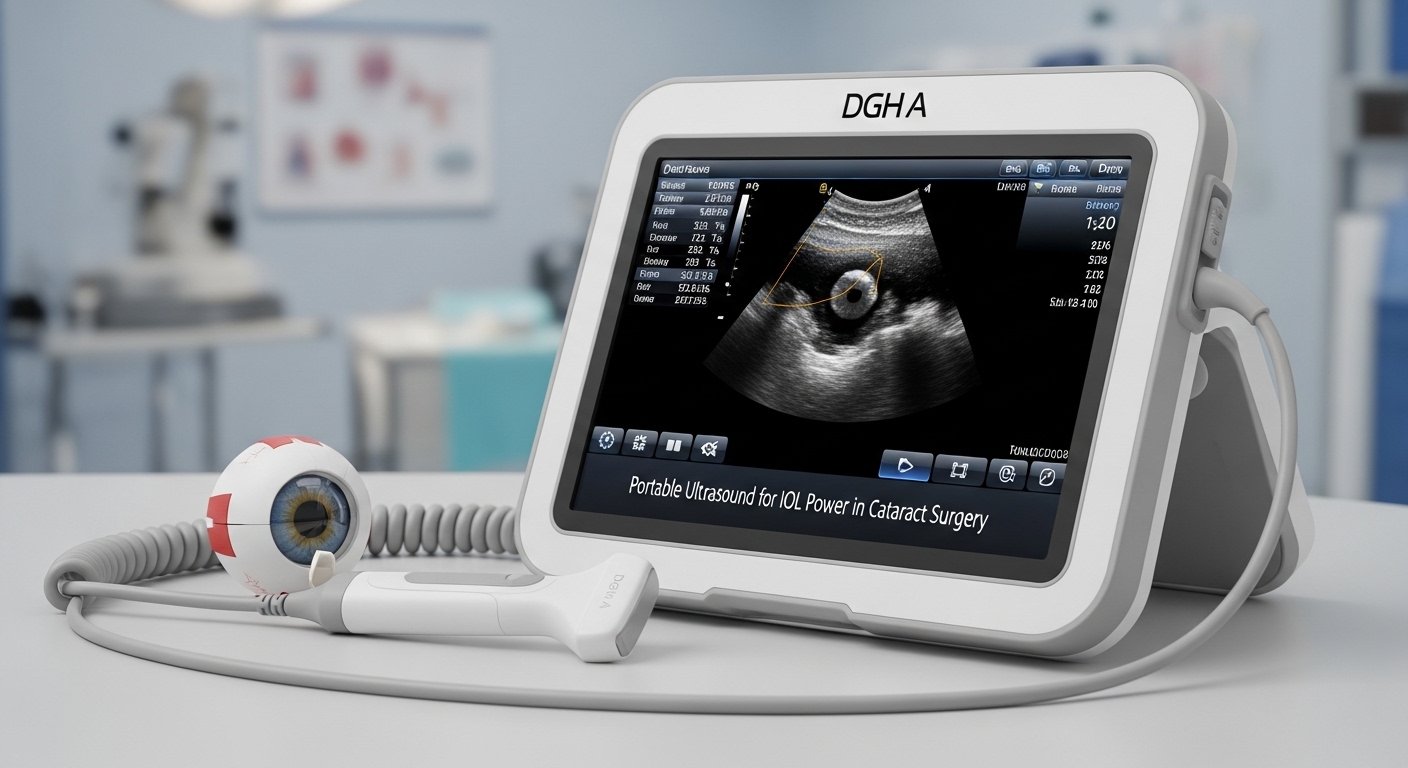
In recent years, advancements in technology have transformed how eye care professionals approach IOL power calculations. One such innovation making waves in the medical community is DGh A—an exciting portable ultrasound device that promises to enhance accuracy while streamlining the surgical process. As we delve into its features and benefits, you’ll discover why DGh A could become an essential tool for cataract surgeons everywhere.
Importance of Accurate IOL Power Calculation
Accurate intraocular lens (IOL) power calculation is critical in cataract surgery. This precision directly impacts visual outcomes for patients. A well-calculated IOL ensures that the lens will provide optimal vision post-surgery.
Inaccurate calculations can lead to complications such as residual refractive errors, necessitating additional procedures. Patients may experience blurred vision or discomfort if their lenses are not properly aligned with their eye’s curvature and diameter.
Surgeons rely on precise measurements to select the correct IOL type and strength. With advances in technology, achieving accuracy has become more feasible than ever before.
The right IOL power means fewer follow-up visits for adjustments or corrections, enhancing patient satisfaction. In a field where every detail counts, investing time in accurate measurements significantly benefits both the surgeon and the patient’s overall experience during cataract surgery.
Traditional Methods of IOL Power Calculation
Traditional methods of IOL power calculation have been the mainstay in cataract surgery for years. Surgeons typically rely on formulas like the SRK/T, Hoffer Q, or Holladay 1 to estimate the appropriate intraocular lens strength based on various eye measurements.
These calculations depend heavily on precise biometry data such as axial length and corneal curvature. Slight discrepancies can lead to significant errors in lens selection, impacting patient outcomes.
Additionally, these methods usually require complex equipment and manual input that adds time to the surgical process. While many surgeons trust their experience with these calculations, variations in individual anatomy can complicate matters further.
Even though traditional methods have proven effective over time, they are not foolproof. The limitations present a compelling case for exploring more innovative solutions tailored specifically for enhanced accuracy and efficiency in IOL power determination.
Introducing DGh A: The Portable Ultrasound Device
The DGh A is revolutionizing the way cataract surgery practitioners approach intraocular lens (IOL) power calculations. Unlike traditional methods, this portable ultrasound device offers unparalleled convenience and accuracy.
Compact and lightweight, the DGh A can be easily transported between clinics or even brought to patients’ homes. This flexibility allows for on-the-spot assessments without compromising precision.
Equipped with advanced technology, the device simplifies complex measurements needed for IOL power determination. Its user-friendly interface ensures that ophthalmologists can quickly grasp its functionalities, streamlining workflow during busy surgical days.
Moreover, DGh A maintains high standards of imaging quality, producing reliable results essential for successful outcomes in cataract surgeries. With a focus on portability and efficiency, it stands out as an invaluable tool in modern ophthalmology practices.
Features and Benefits of DGh A
The DGh A portable ultrasound device revolutionizes IOL power calculation in cataract surgery. Its compact design allows for easy transport, making it ideal for various clinical settings.
Equipped with advanced imaging technology, DGh A delivers precise measurements. Surgeons can trust its accuracy to enhance patient outcomes significantly.
User-friendly interfaces enable quick operation and reduce training time. This feature ensures that medical staff can seamlessly integrate the device into their workflow without disruption.
Moreover, DGh A boasts battery longevity, allowing extended use during surgical procedures or consultations. The wireless capabilities streamline data sharing and storage options, enhancing collaboration among healthcare professionals.
Its durability means minimal maintenance costs over time. Clinics will find that investing in this technology pays off by improving efficiency while maintaining high standards of care for patients undergoing cataract surgery.
Clinical Study Results and Success Rates
Recent clinical studies have showcased the impressive performance of DGh A in cataract surgery. Surgeons using this portable ultrasound device reported highly accurate IOL power calculations.
In one notable study, patients experienced a significant reduction in refractive surprises post-surgery. The success rate for achieving target refraction was over 90%. This remarkable statistic highlights DGh A’s potential to enhance patient outcomes.
Moreover, surgeons appreciated the ease of use that DGh A offers during procedures. Its portability allows for quick assessments without interrupting workflow.
Feedback from medical professionals emphasized confidence in results obtained with this technology. Many noted improved surgical precision and patient satisfaction following operations performed using DGh A measurements.
With such promising data emerging from various trials, it’s clear that integrating this device into standard practice could redefine how cataract surgery is approached moving forward.
Cost Comparison with Traditional Methods
When evaluating the cost of cataract surgery, traditional methods often involve substantial expenses. This includes not only the equipment but also maintenance and training for staff to use these complex systems effectively.
In contrast, DGh A presents a more economical solution. Its portable design minimizes overhead costs associated with large machinery. The reduced need for extensive facility modifications further enhances its affordability.
Training time is significantly shorter with DGh A as well. Healthcare professionals can quickly adapt to using this device, translating into lower labor costs overall.
Additionally, faster patient throughput is achieved due to the efficiency of DGh A’s measurements. This means clinics can handle more patients in less time, maximizing revenue without sacrificing quality care.
Choosing DGh A could lead to significant savings while maintaining accurate IOL power calculations during cataract procedures.
Potential Impact on Cataract Surgery Practices
The introduction of DGh A into cataract surgery practices could revolutionize the way surgeons approach lens implantation. With its portable design, this device allows for greater flexibility in various clinical settings. Surgeons can now perform accurate IOL power calculations right at the bedside or in outpatient clinics.
This accessibility ensures that more patients receive timely treatment without delays caused by equipment limitations. The ease of use means that even less experienced practitioners can confidently utilize it, enhancing overall surgical outcomes.
Moreover, as data accumulates on DGh A’s effectiveness, we may see shifts in training protocols and methodologies across ophthalmology programs. Emphasis will likely move towards integrating advanced technology like this into routine practice.
Incorporating DGh A could also lead to increased patient satisfaction as procedures become quicker and results improve. As a result, healthcare providers might find themselves better equipped to meet rising demands within ocular care while maintaining high standards of precision.
Future Developments and Advancements in DGh A Technology
The future of DGh A technology looks promising, with ongoing research focusing on enhancing its ultrasound capabilities. Developers are exploring advanced imaging techniques that could improve the precision of IOL power calculations.
Integration with AI is another exciting frontier. By harnessing artificial intelligence, DGh A can potentially analyze data faster and more accurately than ever before. This would streamline the process for surgeons, allowing them to make quicker decisions during cataract procedures.
Moreover, expanding connectivity options may enable real-time sharing of data among medical professionals. This collaboration could foster improvements in surgical outcomes globally.
Battery life and portability remain priorities as well. As devices become lighter and easier to transport, they will be even more valuable in various healthcare settings.
With these advancements on the horizon, DGh A stands poised to revolutionize cataract surgery practices worldwide.
Conclusion
The introduction of DGh A represents a significant advancement in cataract surgery technology. With its portable ultrasound capabilities, this device transforms how surgeons calculate intraocular lens (IOL) power. The importance of accurate IOL power calculation cannot be overstated; it directly influences patient outcomes and satisfaction.
Traditional methods have served well over the years, but they come with limitations that can hinder precision. DGh A addresses these gaps by offering enhanced portability and ease of use, allowing for more flexibility in surgical settings. Surgeons now have access to advanced features that streamline their workflow while improving accuracy.
Clinical studies have shown promising results with DGh A, highlighting increased success rates compared to traditional techniques. This not only benefits patients through better visual outcomes but also reduces the potential need for follow-up procedures—ultimately leading to cost savings.
As cataract surgery evolves, integrating devices like DGh A could change standard practices across the board. Embracing this technology paves the way for improved patient care and efficiency within surgical teams.
Looking ahead, continued advancements in DGh A’s technology will likely enhance its capabilities further. Innovations could lead to even more precise measurements or integration with artificial intelligence for predictive analytics.
This evolution points towards a future where cataract surgeries are performed with unprecedented accuracy and confidence.